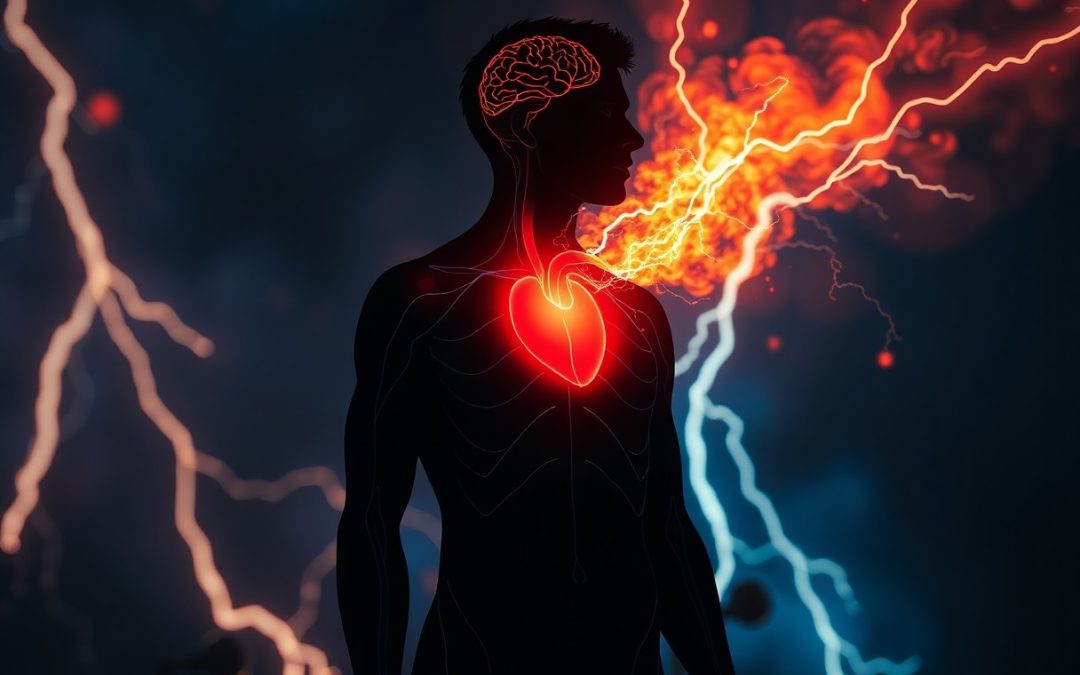
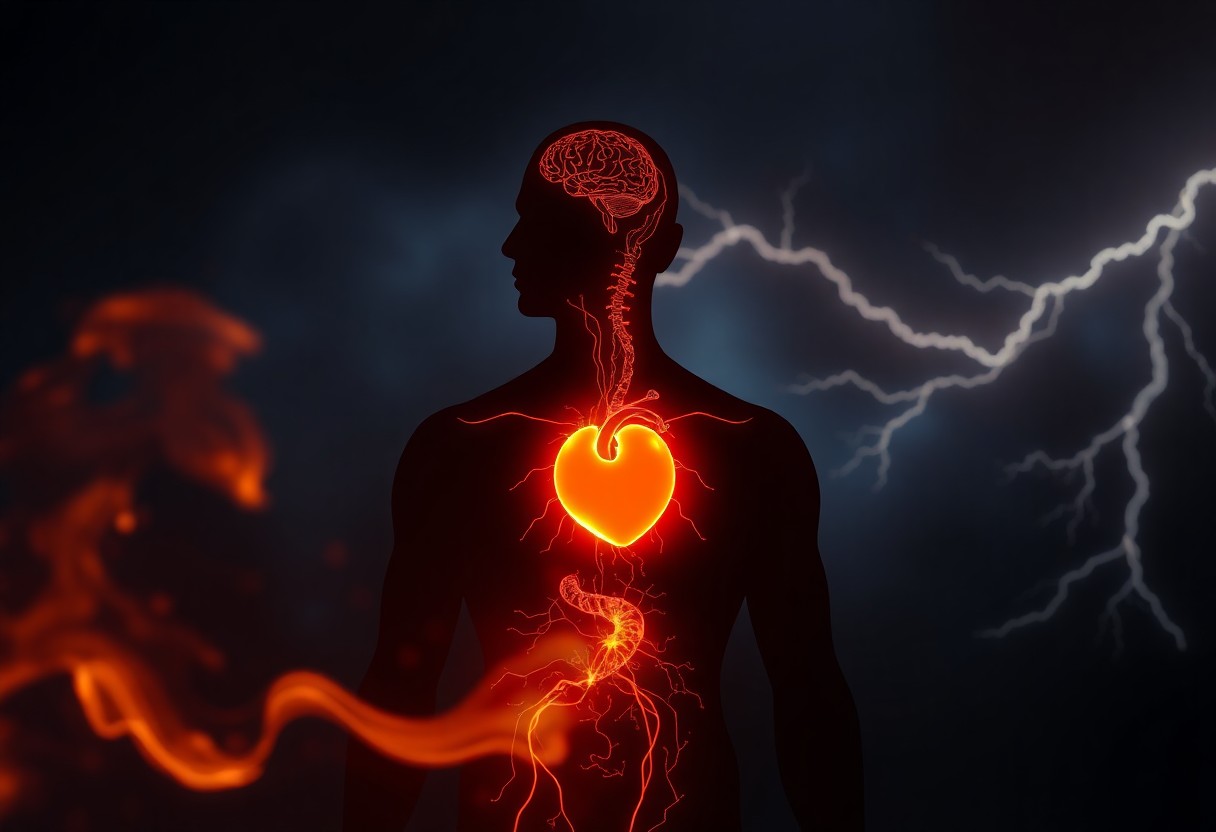
You may not realize that your anger can have serious consequences for your body. Chronic anger can lead to a range of issues, impacting your health and well-being. From straining your heart to disrupting your digestion, the effects of anger can be both immediate and long-lasting. Understanding these consequences is necessary to managing your emotions and promoting better health. Here, we explore five major effects of anger on your body.
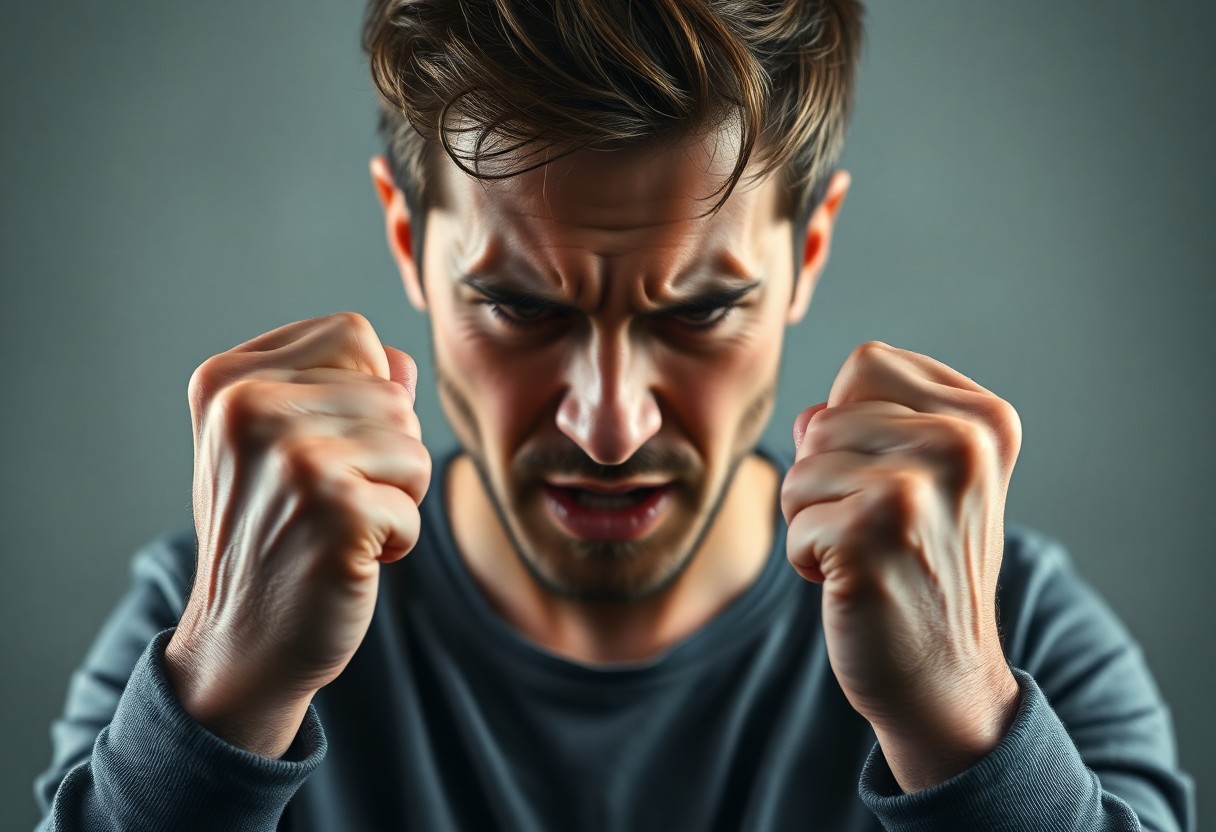

The Physiological Impact of Anger
Anger is a powerful emotional response that triggers a series of physiological changes in your body. When you experience anger, your body prepares itself for a fight-or-flight response, leading to various impacts that affect your overall well-being and health. These changes can manifest in physical symptoms and long-term consequences, particularly if left unaddressed.
Stress Response and Hormonal Changes
Before plunging into the effects of anger on your body, it’s crucial to understand the stress response it activates. Anger elicits a surge of stress hormones, such as adrenaline and cortisol, flooding your system as your body gears up to react. This physiological response can lead to heightened energy levels, but when chronic, ultimately takes a toll on your overall health.
Effects on Heart Health
Before considering the broader implications of anger, it’s beneficial to focus on its specific impacts on heart health. Frequent and intense anger can contribute to irregular heartbeats and increase your risk of serious conditions such as heart attacks. Studies show that people who often experience intense anger face a significantly heightened risk of having a heart attack compared to those who manage their anger more effectively.
Also, the connection between anger and heart health is alarming: Engaging in anger can lead to a rise in blood pressure and stress on the cardiovascular system. This intensification of heart workload increases the likelihood of suffering from heart attacks or developing arrhythmias. It’s crucial to address your anger management strategies, as chronic anger can have dangerous consequences for your health and well-being.
Anger’s Connection to Heart Attacks
It is important to understand that anger is linked to a significantly higher risk of heart attacks. When you experience intense anger, your body releases stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, which can strain your heart and vascular system. Studies indicate that episodes of anger can lead to acute cardiac events, especially if you already have underlying heart conditions. By managing your anger effectively, you can help protect your heart health and reduce the likelihood of serious health complications.
Digestive Disruptions Due to Anger
Assuming you often find yourself feeling angry, it’s important to understand how this emotion can disrupt your digestion. When anger triggers your body’s fight-or-flight response, it diverts blood flow away from your digestive system, which can lead to issues such as nausea, bloating, or even stomach pain. Chronic anger can exacerbate these symptoms, potentially leading to long-term complications that affect your overall health. By managing your anger, you can help maintain a healthier digestive system and improve your health overall.
Mental Health Consequences of Chronic Anger
Clearly, chronic anger can severely impactyour mental well-being. You may experience difficulties in maintaining relationships due to irritability and frustration, which can lead to isolation. Research indicates that too much anger can set the stage for harmful behaviors, affecting your emotional stability. Additionally, unresolved anger can contribute to a higher risk of developing mental health issues like anxiety and depression. Understanding these consequences is imperative for achieving a balanced and healthier emotional state. Prioritize your health by seeking effective coping strategies.
The Connection Between Anger and Sleep Disturbances
Now, you may not realize that anger can significantly impact your sleep patterns. When you experience intense or prolonged anger, your body remains in a heightened state of stress, which can lead to difficulties in falling asleep or staying asleep. This chronic activation of stress hormones, such as adrenaline and cortisol, not only affects how well you rest but can also contribute to serious health issues over time. By managing your anger effectively, you can improve both your mental well-being and your quality of sleep.
Strategies for Managing Anger
Not managing your anger effectively can lead to severe consequences for both your physical and mental health. You can employ several strategies to keep your anger in check. Begin by practicing deep breathing or mindfulness techniques to reduce immediate stress responses. Engaging in regular physical activity can also help mitigate the effects of anger on your body by lowering levels of stress hormones. Consider seeking support through therapy or counseling to develop healthier coping mechanisms. Your relationships and overall health will benefit significantly from these positive changes.
Final Words
On the whole, understanding the effects of anger on your body can help you manage your emotional responses more effectively. Anger can stress out your heart, increase your risk of heart attacks, disrupt digestion, hinder your mental well-being, and interfere with your sleep. By acknowledging these impacts, you can take proactive steps to mitigate anger’s grip on your life, ultimately leading to better overall health.
FAQ
Q: What are the physical effects of anger on the heart?
A: Anger can physically stress out the heart due to the release of stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol. This stress response can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure, making the heart work harder. Over time, this can contribute to serious cardiovascular issues. Additionally, anger has been shown to affect those with arrhythmias, heightening the risk of further heart complications. For more information on how emotions can impact your overall health, consult with a medical professional.
Q: How does anger affect digestive processes?
A: Anger can disrupt digestion by causing the body to enter a fight-or-flight response, leading to decreased blood flow to the digestive system. This can result in symptoms like stomach cramps, nausea, or even gastrointestinal disorders. Living with chronic anger may therefore lead to long-term digestive issues, emphasizing the importance of managing emotional responses for better health. Seeking appropriate coping strategies can help mitigate these effects.
Q: What impact does anger have on sleep quality?
A: Anger can significantly interfere with sleep quality. When a person is angry, their body is often in a heightened state of arousal, which can make it difficult to relax and fall asleep. Additionally, racing thoughts related to anger can lead to insomnia or interrupted sleep patterns. For those struggling with sleep due to anger or other emotions, reaching out for support may enhance overall health and well-being.