There’s a growing interest in sustainable food sources, and you might be surprised to discover the remarkable benefits of seaweed farming. This often-overlooked ocean plant not only contributes to environmental health but also offers numerous nutritional advantages that can enhance your well-being. By understanding the positive impact of seaweed farming on both the planet and your health, you’ll be equipped to make informed dietary choices that align with a sustainable lifestyle.

Understanding Seaweed
Understanding the world of seaweed requires some insight into its various aspects and benefits. As one of the most nutrient-rich foods available, seaweed serves not just as a food source, but also plays an important role in sustainable farming practices. This chapter will help you navigate through its types and nutritional profile to better appreciate its potential implications on health and the environment.
Overview of Seaweed
To appreciate the significance of seaweed, it’s necessary to understand that it has been an integral part of human diets and ecosystems for thousands of years. Known for its versatility in culinary applications and numerous health benefits, seaweed is also emerging as a sustainable solution to various environmental issues.
Types of Seaweed
To make informed choices about incorporating seaweed into your diet, it’s important to recognize the different types available. Common categories include:
- Nori
- Kelp
- Wakame
- Arame
- Dulse
This variety offers many flavors and textures that can elevate your culinary experience.
| Type | Characteristics |
| Nori | Used mainly for sushi, it’s a red algae that’s popular in Asian cuisine. |
| Kelp | A large brown algae that is rich in vitamins and typically found in colder waters. |
| Wakame | Commonly used in miso soup, this edible seaweed is known for its delicate taste. |
| Arame | A sweet kelp with a firm texture, often used in salads and side dishes. |
| Dulse | A red algae that can be eaten as a snack or added to various dishes. |
For instance, each type of seaweed brings unique flavors and nutritional profiles to your meals. You may want to try incorporating them into salads, soups, or snacks to explore their culinary versatility.
- Each type has its own specific health benefits.
- Some are rich in iodine, while others provide necessary vitamins.
- Sea vegetables are great for texture and flavor in dishes.
- They can be consumed fresh, dried, or powdered.
- This variety is what makes seaweed a valuable addition to your diet.
Nutritional Profile
With an impressive range of nutrients, seaweed is often considered a superfood. It’s particularly known for its high iodine content and various vitamins and minerals necessary for overall health.
Due to its nutrient density, seaweed is a powerhouse of necessary vitamins and minerals, including iron, magnesium, and vitamins K and A. For instance, raw kelp provides significant percentages of daily values for these nutrients, making it a worthy addition to your meals.
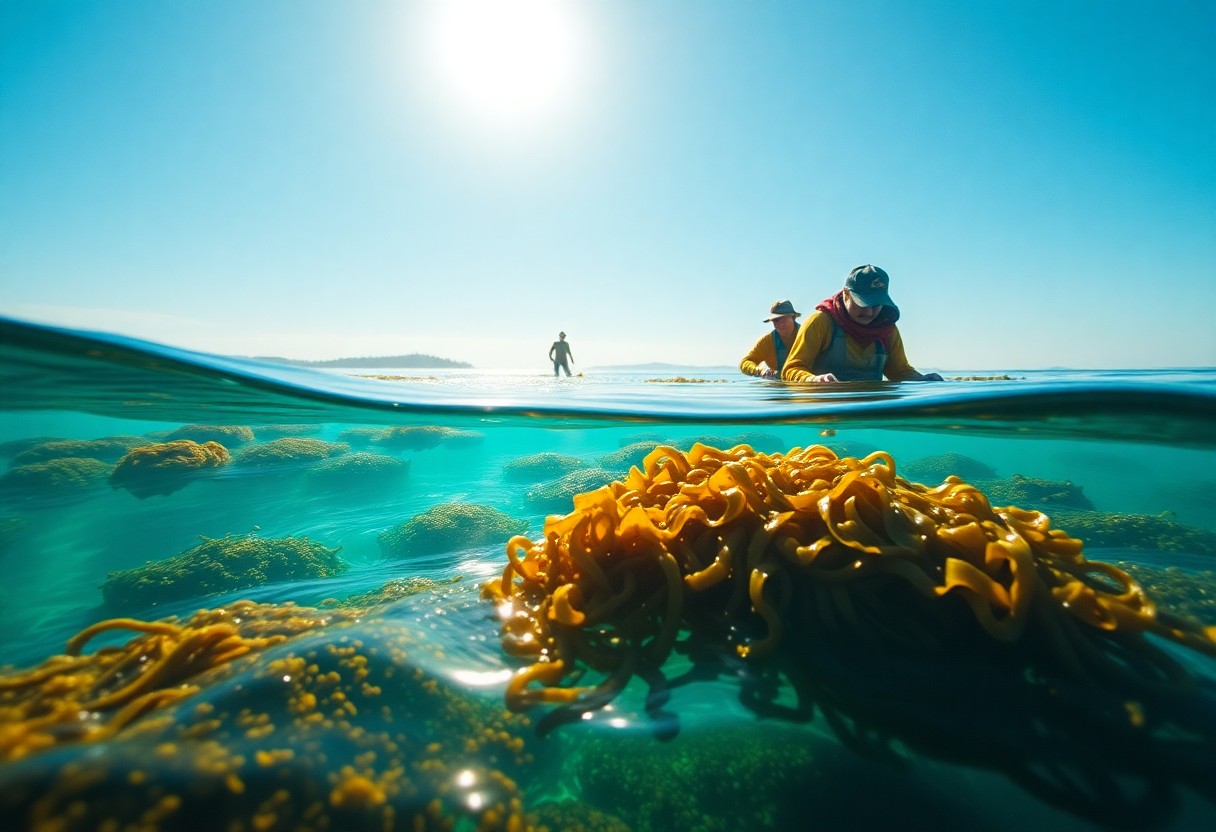
The Science of Seaweed Farming
Any discussion of the sustainable benefits of seaweed farming begins with understanding what it is.
What is Seaweed Farming?
Behind the scenes, seaweed farming involves cultivating various types of seaweed in oceanic environments, typically utilizing ropes or nets suspended in the water column. This method allows the algae to thrive by harnessing nutrients from seawater, all while requiring no additional resources like freshwater, pesticides, or fertilizers.
Methods of Cultivation
Against traditional agricultural techniques, seaweed farming employs innovative methods that capitalize on the natural growth cycles of seaweed. Different cultivation practices can include longlines, rafts, or integrated multi-trophic aquaculture, where multiple species, such as fish and shellfish, are farmed alongside seaweed to optimize ecosystem health and resource use.
For instance, longline cultivation uses horizontal lines anchored to the seabed, from which seaweed is suspended. This method allows for widespread growth and is particularly effective for larger species like kelp. Raft systems can support various seaweed types and help diversify ecosystem benefits, including enhanced biodiversity and improved water quality.
Environmental Requirements
Cultivation of seaweed thrives in specific environmental conditions. These include clean, nutrient-rich waters with adequate light exposure and appropriate temperatures, often found in coastal areas. Seaweed can grow in diverse environments, from shallow coastal waters to deeper ocean expanses.
But, the environmental requirements of seaweed farming also mean you need to consider factors such as water quality and temperature stability. Optimal growth conditions generally fall within certain thresholds; for example, many species prefer temperatures between 10°C to 20°C. The local marine ecosystem’s health impacts not only the growth of seaweed but also influences its nutritional content, making it imperative to maintain balanced water conditions.
Ecological Benefits of Seaweed Farming
For a sustainable future, understanding the ecological benefits of seaweed farming is vital. This natural resource not only supports environmental health but also contributes to combating climate change and enhancing marine ecosystems.
Carbon Sequestration
On a significant scale, seaweed captures carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and stores it in the ocean, which helps mitigate climate change. By absorbing carbon during photosynthesis, seaweed farming reduces greenhouse gas levels, contributing to a healthier planet.
Habitat Restoration
To strengthen marine environments, the cultivation of seaweed provides habitats for various ocean-dwelling species. This farming creates rich ecosystems that enhance biodiversity, offering refuge and sustenance for fish and other wildlife.
A study by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration emphasizes that seaweed farms can significantly contribute to marine life recovery. By adding structural complexity to coastal areas, they create safe nurseries for young fish and other organisms, promoting overall ocean health.
Nutrient Filtration
Against the backdrop of ocean pollution, seaweed farming plays a vital role in nutrient filtration. It absorbs excess nitrogen and phosphorus from the water, which are often byproducts of agricultural runoff and waste.
With this nutrient filtration, seaweed helps improve water quality and combat issues like algal blooms, which can be harmful to marine ecosystems. By integrating seaweed farming practices, you contribute not only to your health but also to the overall health of our oceans.
Economic Advantages
Now, let’s explore how seaweed farming can positively impact local economies and create job opportunities.
Job Creation and Local Economies
For many coastal communities, seaweed farming presents a unique opportunity for job creation. As demand for sustainable food sources grows, local farms can thrive, providing employment in harvesting, processing, and distribution.
Opportunities for Fishing Communities
At the same time, seaweed farming offers fishing communities a chance to adapt to changing ocean conditions. As traditional fishing stocks decline, diversifying into seaweed cultivation can help these communities remain economically viable.
But the transition to seaweed farming doesn’t just support economic stability; it also allows fishing families to leverage their existing knowledge of maritime ecosystems. By utilizing their skills in a new sector, they can ensure their livelihoods remain sustainable in the face of climate change and oceanic shifts.
Reducing Dependency on Imported Seaweed
Local seaweed farming significantly reduces dependency on imported products. The U.S. currently imports nearly all its seaweed, leading to lost economic opportunities for domestic producers.
Further, by fostering a homegrown seaweed industry, you can enjoy fresher products with a lower environmental impact. Supporting local growers not only boosts your economy but also ensures that you contribute to responsible labor practices and sustainable farming techniques. Investing in domestic seaweed farming can set a positive precedence aimed at more resilient food systems.
Health Benefits of Seaweed
Despite the growing popularity of many superfoods, few can match the comprehensive health benefits that seaweed offers. This nutrient-rich marine plant not only provides necessary vitamins and minerals but also supports your health through its unique bioactive compounds and medicinal properties. Its integration into your diet can yield significant advantages for both body and mind.
Nutritional Value
Among the many types of seaweed, varieties like kelp and wakame are particularly rich sources of vital nutrients. Kelp contains about 55% of your daily value (DV) of vitamin K1 and 45% of folate per 100 grams, while wakame offers an astounding 280% of your DV of iodine in just two tablespoons. Incorporating these nutrient-dense foods into your meals can greatly enhance your overall nutritional intake.
Bioactive Compounds and Their Functions
Along with its impressive nutritional profile, seaweed is rich in bioactive compounds that provide various health benefits. These compounds include antioxidants, polyphenols, and necessary fatty acids, which collectively contribute to improved health outcomes.
Nutritional studies indicate that these bioactive compounds can play a significant role in protecting your body from oxidative stress and inflammation. For example, antioxidants found in seaweed help combat free radicals, thereby promoting cellular health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Furthermore, some studies have suggested that specific compounds within seaweed can even aid in weight management and improve metabolic health.
Medicinal Uses
Uses of seaweed for medicinal purposes have been recognized for centuries. It is known for its antioxidant, antimicrobial, and neuroprotective properties, making it a valuable addition to any health-conscious diet.
But the potential benefits don’t stop there. Research indicates that certain compounds in seaweed have demonstrated promising anticancer properties, showing the ability to induce cell death in cancer cells and inhibit metastasis. This aligns with its traditional use in folk medicine, highlighting seaweed as not just a food source, but also as a powerful ally in health optimization.
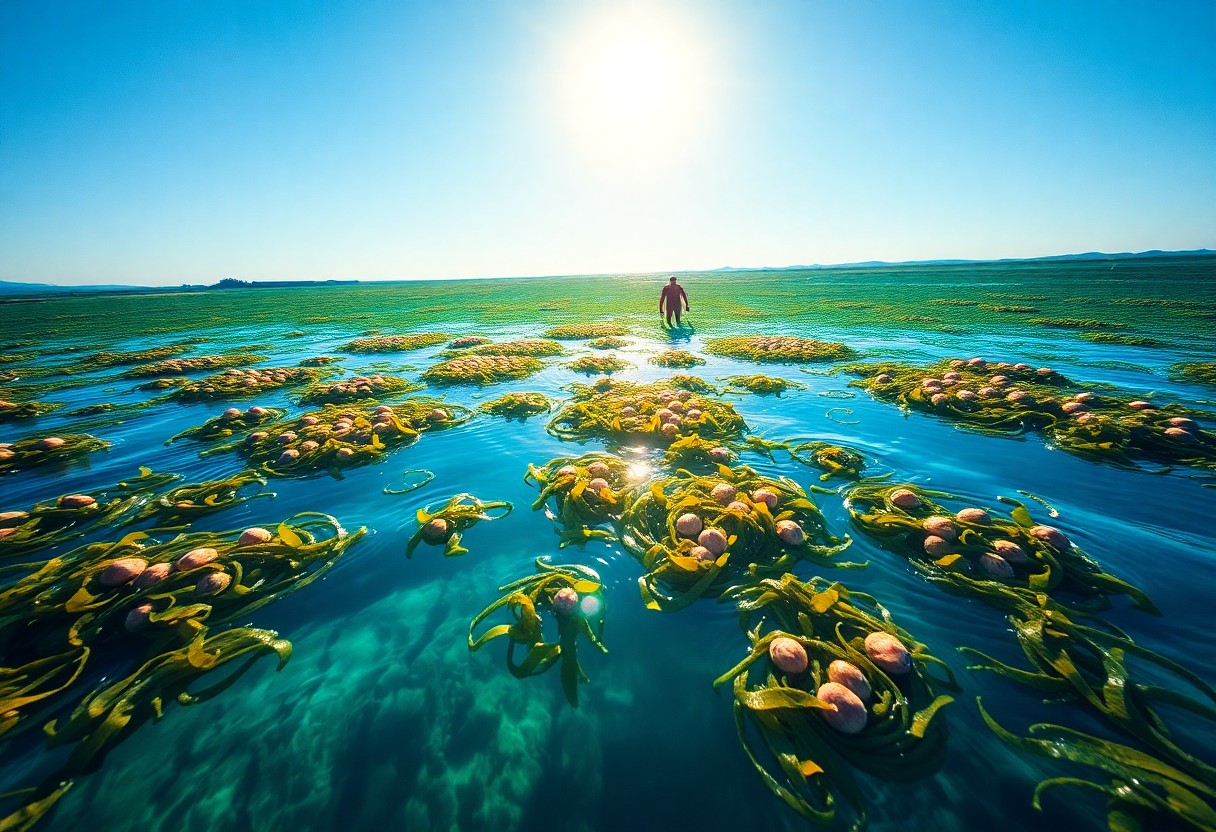

Potential Downsides
All foods come with their pros and cons, and seaweed is no exception. As you explore the benefits of this sustainable superfood, it’s important to be aware of the potential downsides that can affect your health and the environment.
Iodine Levels and Health Risks
At its best, seaweed is a rich source of iodine; however, excessive consumption can pose health risks. Eating iodine-rich seaweeds like kelp regularly may lead to an excess of iodine, which can negatively impact thyroid function, especially in individuals with existing thyroid conditions or in pregnant women.
Environmental Concerns of Farming
On the other hand, while seaweed farming is touted for its ecological benefits, it is not without drawbacks. Increased farming activities can introduce risks such as whale entanglement due to farming gear and pollution from lost or discarded gear, which may adversely affect marine ecosystems.
This environmental impact highlights the need for responsible seaweed farming practices. Ensuring that farms are managed properly can mitigate these risks and protect marine wildlife. Sustainable farming techniques are vital to maintain the balance between harvests and the health of our oceans, ensuring that seaweed cultivation contributes positively to ecosystems rather than harming them.
Accessibility and Affordability Issues
At present, while you may find affordable seaweed options at Asian grocery stores, it may soon become a high-cost item. The growing popularity of seaweed in upscale markets may limit access for many consumers.
Concerns regarding accessibility and affordability highlight a potential barrier to widely adopting seaweed into your diet. The majority of seaweed sold in the U.S. comes from wild harvesting or small farms, often targeting niche markets. While this can support local economies, it may also mean that fresh, domestically grown options remain out of reach for the average consumer, particularly when imports may carry additional environmental and ethical issues.
The Sustainable Health Benefits of Seaweed Farming Explained
Now that you understand the myriad benefits of seaweed farming, it’s clear that incorporating this sustainable superfood into your diet can positively impact both your health and the environment. You can enjoy its rich nutritional profile while supporting healthy oceans and fostering economic resilience within coastal communities. As you explore ways to include seaweed in your meals, consider the ecological and social benefits that come with this ancient food source.