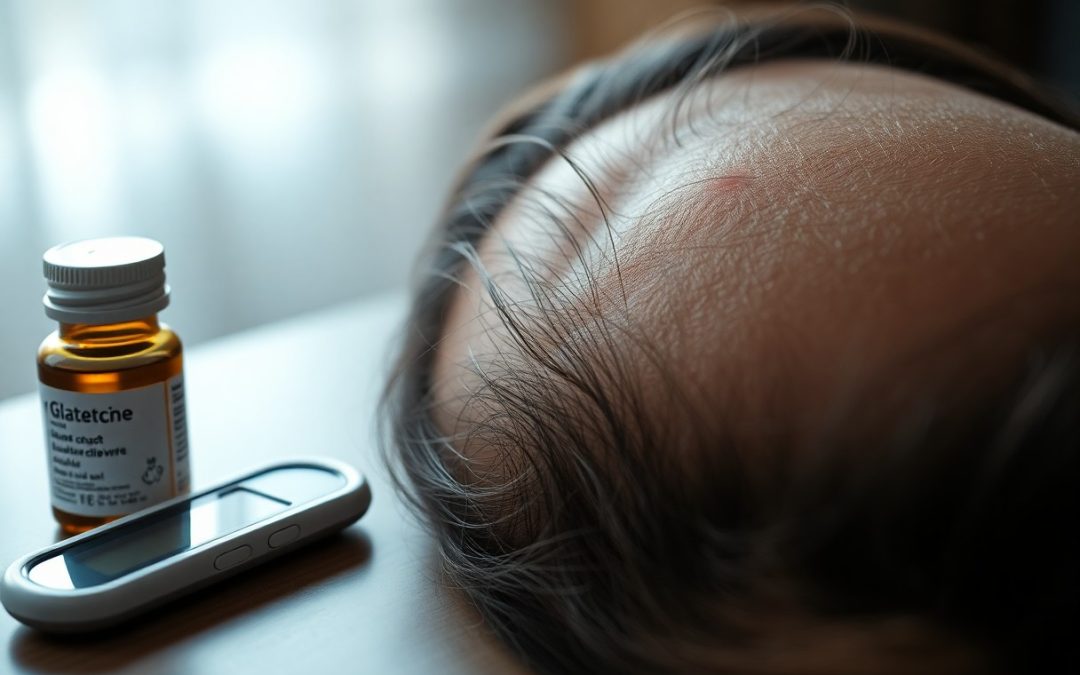
It’s important to recognize that if you have diabetes, you may experience abnormal hair loss due to high blood sugar levels. This condition can influence the blood vessels that supply your hair follicles, resulting in hair loss. Various factors associated with diabetes complications, such as autoimmune issues and hormonal imbalances, can exacerbate the problem. Being aware of these potential links is crucial for protecting your overall health and taking proactive steps to manage your hair loss effectively.
Overview of Hair Loss
For those living with diabetes, experiencing hair loss can be a concerning symptom that may signal underlying health issues. Diabetes can influence various skin and hair conditions due to factors such as poor blood circulation and hormonal imbalances. While some hair shedding is normal, it’s important to understand the difference between typical hair loss and more severe forms that could indicate additional complications related to your diabetes management.
Natural Hair Shedding vs. Hair Loss
Shedding is part of the natural hair growth cycle, where strands fall out to make way for new growth. Typically, losing about 50 to 100 hairs a day is considered normal. However, if you notice an increase in shedding beyond this range or experience bald patches, it may indicate a more significant issue requiring your immediate attention.
Signs of Serious Hair Loss
Loss of hair can be alarming, especially when it occurs suddenly or in larger clumps than usual. If you observe bald patches, thinning hair, or a noticeable change in your overall hair density, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional. Such symptoms could point to more serious underlying conditions linked to your diabetes, as well as other factors, necessitating early intervention for effective treatment.
Hence, recognizing these signs early is beneficial. If you find your hair loss escalating or accompanied by other symptoms, such as skin irritation or changes in your overall health, it is important to seek help. An early assessment can lead to appropriate health interventions, maximizing potential recovery and preserving your existing hair.

Relationship Between Diabetes and Hair Loss
Assuming you have diabetes, it’s important to be aware that your condition may influence hair loss. While researchers have not definitively linked high blood sugar levels directly to hair loss, diabetes is associated with several risk factors that can contribute to excessive shedding. This indicates that managing your diabetes effectively may not only benefit your overall health but also support your hair’s vitality.
Poor Blood Circulation
Beside the hormonal and metabolic changes caused by diabetes, poor blood circulation may also impact your hair growth. Reduced blood flow to the scalp could lessen the nutrients and oxygen necessary for healthy hair follicles, potentially leading to thinning or hair loss. Enhancing your circulation through lifestyle changes may thus promote healthier hair.
Autoimmune Conditions
About 30% of individuals with diabetes may experience autoimmune conditions, which can further exacerbate hair loss. Conditions such as alopecia areata can cause your immune system to attack hair follicles, resulting in patches of hair loss. Understanding this relationship helps you recognize when to seek medical advice, especially if you notice significant changes in your hair density.
This is where you should take notes: autoimmune conditions related to diabetes can pose more serious threats to your hair. If you notice sudden or patchy hair loss, immediate consultation with a healthcare professional is critical to determine the underlying causes. Addressing these health challenges early can lead to more effective treatment options and prevent further progression of hair loss.

Diabetes Medications and Hair Loss
Clearly, certain diabetes medications may contribute to hair loss, especially as they interact with your body’s hormonal and vascular systems. Among these medications, GLP-1 agonists, commonly prescribed for managing type 2 diabetes, have been reported to cause hair thinning in some patients. If you notice unexpected hair loss while on these medications, consult your healthcare provider to consider alternative options or adjustments to your treatment plan.
Impact of GLP-1 Agonists
Diabetes medications like GLP-1 agonists, including semaglutide (Ozempic), can lead to hair loss in some patients. This side effect may stem from hormonal shifts as your body adjusts to improved insulin sensitivity. If you experience noticeable changes in hair density or have concerns, it’s important to discuss this with your doctor.
Other Medication Effects
One potential concern with diabetes medications is their effect on hair health beyond hormonal changes. Even with treatments that improve blood sugar control, such as medications for hypertension or cholesterol, you should be aware of potential side effects. While many of these medications are necessary for maintaining your overall health, they can sometimes lead to hair loss or thinning. Monitoring your hair’s condition and consulting your physician can help navigate these side effects effectively and safeguard both your hair and well-being.
Associated Conditions
Once again, diabetes can lead to hair loss through a variety of associated conditions. These include thyroid disorders, iron deficiency, and polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), all of which can further complicate your diabetes management and contribute to hair thinning or loss. It’s important to be aware of these connections so you can address them with your healthcare provider and explore potential treatments.
Thyroid Issues
Below, thyroid issues can significantly impact your hair health. Conditions such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism may result in hair thinning or hair loss, as they can alter hormonal balances and blood circulation necessary for healthy hair growth. If you suspect a thyroid issue, consulting with your healthcare professional for evaluation and treatment can make a positive difference in both your thyroid function and hair vitality.
Iron Deficiency and PCOS
To address iron deficiency and PCOS, it’s crucial to understand how these conditions can influence your hair health. Iron deficiency can limit oxygen delivery to hair follicles, inhibiting growth and leading to hair loss. Simultaneously, PCOS can cause hormonal imbalances, which frequently result in thinning hair. Given the high prevalence of both conditions, especially in women with diabetes, ensuring you have adequate iron levels and managing PCOS can lead to improvements in your overall health and potentially help restore thicker, healthier hair.
Psychological Factors
Your mental wellbeing can significantly impact hair health, especially if you have diabetes. The ongoing challenges of managing blood sugar levels can often lead to feelings of anxiety and depression, both of which are known to exacerbate hair loss. It’s crucial to be aware of the psychological effects diabetes can have on your body and mind:
- Stress management is important for overall health.
- Anxiety can lead to worsening hair loss.
- Depression may result in neglect of self-care.
Thou must prioritize mental well-being to help mitigate hair loss associated with diabetes.
Stress and Hair Shedding
To effectively tackle hair shedding linked to stress, you should first identify and manage sources of stress. Studies suggest that high-stress levels can significantly contribute to hair loss, particularly in individuals with diabetes. Maintaining a balanced lifestyle with regular exercise, healthy nutrition, and relaxation techniques can be beneficial. Consulting a healthcare professional can help you navigate your mental health and its relationship with hair shedding. Thou must take proactive steps to minimize the impact of stress on your hair health.
Management Tips for Diabetic Hair Loss
Keep your hair healthy by adopting effective management strategies to tackle diabetic hair loss. Consider the following:
- Maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Incorporate a diet rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Explore medications like minoxidil.
- Practice stress-reduction techniques.
Recognizing early signs of hair loss can aid in timely intervention and care.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Beside self-care, seeking guidance from a healthcare professional is advisable. A board-certified dermatologist can evaluate your hair loss symptoms and recommend appropriate tests or treatments. Identifying potential underlying issues promptly can significantly impact your hair health and recovery.
Treatment Options
Consulting with your doctor about treatment options can help address diabetic hair loss effectively. Several medications are available to aid hair growth, including minoxidil, which increases blood flow to hair follicles. Additionally, tests for nutrient deficiencies in vitamin D, B12, zinc, and iron may guide further treatment decisions. Discussing the potential side effects of medications with your doctor ensures you make informed decisions about your care.
Tips for using minoxidil include applying it consistently for at least six months to observe results. You should also be aware that some medications may have side effects, so monitoring your health while starting new treatments is necessary. A holistic approach involving a balanced diet, stress management, and regular medical check-ups will help maintain your hair health as part of your overall well-being.
To wrap up
Summing up, if you have diabetes and are experiencing hair loss, it may be linked to factors such as poor blood circulation, autoimmune conditions, or hormonal imbalances. It’s imperative to monitor your condition and consult a healthcare professional to identify potential underlying issues. Taking timely action can improve your hair health and overall well-being. By addressing these concerns, you can better manage your diabetes and its effects on your health.
FAQ
Q: Can diabetes directly cause hair loss?
A: While researchers are still exploring the direct link between diabetes and hair loss, it is known that diabetes can lead to several factors that increase the risk of hair loss. High blood sugar levels can affect blood circulation, reducing the flow to hair follicles, thereby hindering hair growth. Additionally, diabetes is often associated with autoimmune disorders and hormonal imbalances, both of which can contribute to hair loss.
Q: What specific mechanisms within diabetes might lead to hair loss?
A: There are several mechanisms through which diabetes may cause hair loss. Poor blood circulation is a primary factor, as reduced blood flow to the scalp can limit nutrient delivery to hair follicles. Furthermore, individuals with diabetes may experience conditions such as thyroid issues and iron deficiency, which are also linked to hair loss. Stress associated with managing diabetes can exacerbate hair shedding as well.
Q: What can individuals with diabetes do to manage hair loss?
A: People with diabetes experiencing hair loss should consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment options. Medications like minoxidil may be effective, as they stimulate hair growth and improve blood flow to the scalp. Dietary supplements that address vitamin and mineral deficiencies could also be beneficial. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as reducing stress, maintaining stable blood sugar levels, and considering styling options can help manage the appearance of hair loss.