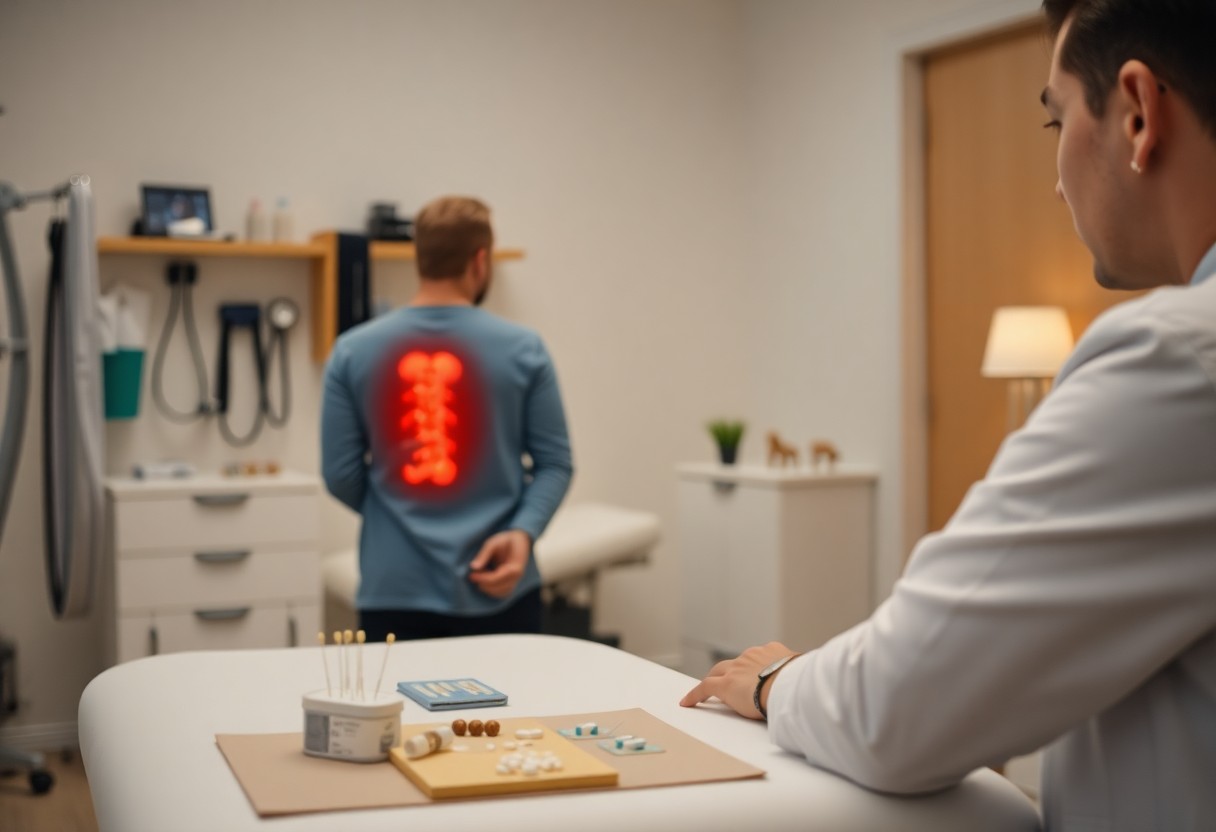
Over a recent analysis of back pain therapies, researchers discovered that many common treatments you may rely on are not as effective as you think. In fact, only a few therapies, such as NSAIDs for acute pain, showed any real benefit, and even then, the results were often modest. This finding highlights the need for a tailored approach to your health, emphasizing that there is no one-size-fits-all solution for managing lower back pain.
Effectiveness of Common Treatments
While the search for effective treatments for lower back pain continues, many standard options have proven to be only marginally helpful, according to recent research. Most interventions, including both drug and nondrug therapies, either showed minimal benefits or were ineffective when compared to placebo, highlighting the need for more comprehensive studies to guide your treatment choices.
Analysis of Medications
One significant finding from the study indicated that while nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) were effective for acute low back pain, many common medications like acetaminophen and certain opioids demonstrated little to no benefit, suggesting that their use should be reconsidered in your pain management strategy.
Evaluation of Nondrug Options
Medications have long been the focus of lower back pain management, but you should also explore various nondrug interventions. Research shows that options like exercise, acupuncture, and spinal manipulation are often inconclusive in providing relief, leaving you with limited choices. Meanwhile, other methods, such as behavior education and massage, failed to demonstrate any significant effect for acute pain. For chronic pain, nondrug therapies require further investigation to establish effectiveness and safety. Understanding these options can empower you in selecting a more personalized approach to managing your back pain.

Marginal Benefits of Effective Treatments
If you’re exploring treatment options for lower back pain, it’s necessary to understand that many interventions yield only marginal improvements. Despite the variety of therapies available, research indicates that the benefits often fall short of expectations, leaving patients with modest relief rather than significant outcomes. Understanding these limitations can help you make informed choices about your pain management strategy.
NSAIDs for Acute Back Pain
Below, research shows that nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are effective for acute low back pain, delivering better results compared to placebo treatments. Medications like ibuprofen and naproxen can help manage short-term pain, but it’s important to consider their potential side effects and use them as part of a broader treatment plan.
Therapies for Chronic Back Pain
NSAIDs, while effective for acute low back pain, do not provide the same level of relief for chronic pain. In fact, only five therapies have shown effectiveness for chronic back pain, but these benefits are generally small when compared to placebo. This indicates a need for tailored treatment approaches that address your unique pain experience. It’s vital to collaborate with healthcare providers to find the best strategy suited to your individual needs, as a personalized approach can often yield better results.
Another important factor to consider is that three treatments, including antibiotics and anesthetics, have been found ineffective for chronic pain. Additionally, therapies such as acupuncture and massage have inconclusive evidence regarding their benefits. This underlines the need for rigorous research and the potential for you to seek alternative options that better align with your specific pain mechanisms.
Ineffectiveness of Certain Therapies
One key finding of recent research reveals that many commonly used therapies for lower back pain are ineffective. In particular, pain management methods like exercise, steroid injections, and acetaminophen have been shown to provide little to no relief for acute low back pain. With so many options available, understanding what does not work is just as important as knowing what does when it comes to addressing your pain.
Acute Back Pain Treatments
An analysis indicates that only nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) showed significant effectiveness for acute low back pain when compared to placebo. Treatments like muscle relaxants and opioids lacked sufficient evidence of benefits, signaling the need for more robust approaches in tackling your acute pain.
Chronic Back Pain Treatments
For chronic low back pain, five therapies were demonstrated to be somewhat effective; however, their benefits were modest. Treatments such as exercise and massage may provide some relief, but it’s important to note that many other options, including antibiotics and anesthetics, have proven ineffective. The findings highlight the complexity of chronic pain management, emphasizing that your response to treatment may vary significantly.
Another noteworthy point is that many therapies have inconclusive evidence backing them, meaning that their effectiveness may not be reliable for everyone. Acupuncture, massage, and certain medications have been shown to have variable outcomes in studies. This highlights the importance of finding the right combination of therapies for your unique situation. Keep in mind that personalized approaches in pain management are necessary to improving your overall experience and quality of life.
Individual Responses to Treatments
Despite the findings suggesting limited effectiveness in many treatments for lower back pain, individual responses can vary significantly. While certain therapies may not work for the average patient, they can still provide relief for specific individuals based on their unique pain mechanisms and biological factors. Personalizing your treatment plan could lead to better management of your pain and improved quality of life.
Variability in Effectiveness
Behind the average results of treatments, your individual response can differ widely. As the study indicates, many therapies, such as muscle relaxants and opioids, showed inconclusive evidence for effectiveness. This variation means that while some may derive great benefit from a particular treatment, others may find it ineffective. Understanding this variability is key to managing your own back pain effectively.
Importance of Personalized Medicine
An effective approach to treating lower back pain lies in personalized medicine, which tailors treatment plans to meet your specific needs and preferences. This strategy recognizes that there is no one-size-fits-all solution, and a treatment that is ineffective for one person may yield significant results for another. By exploring a range of options and focusing on your unique experience, you have a better chance of finding a method that truly enhances your quality of life.
In addition, personalized medicine allows for the incorporation of various interventions to address your specific pain profile—whether that involves physical therapy, psychological support, or different medications. By taking a comprehensive view of all these factors, you can improve not just your pain levels but also your health overall. This targeted approach emphasizes the need for a multidisciplinary treatment team that collaborates to design a strategy best suited to your individual scenario.
Multidisciplinary Approaches to Pain Management
Many experts advocate for a multidisciplinary approach to managing lower back pain, which combines physical, psychological, and medical treatments. This comprehensive strategy addresses the complex nature of back pain, considering individual factors, and providing a more tailored solution to enhance your quality of life.
Combining Therapies
Above all, exploring a variety of therapies can yield better results for your back pain. Integrating treatments like physical therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, and medication may help you find the best combination that works for your individual needs, optimizing overall pain management.
Managing Expectations
Beside understanding the benefits of various treatments, it’s important to manage your expectations realistically. While some therapies may provide modest relief, you need to recognize that not every treatment will work for you, as individual responses can significantly vary.
Therapies for lower back pain can often lead to confusion when results are less than satisfactory. You may find that a treatment offers only marginal benefits or even none at all. Hence, maintaining realistic expectations can mitigate frustration. The study indicates that various treatments yield limited success; for instance, NSAIDs showed effectiveness mainly for acute pain, while chronic pain therapy remains less predictable. Focus on finding what specifically improves your well-being, and consult your healthcare provider to adjust your approach as needed.
The Need for Further Research
Once again, the findings from recent studies highlight the complexity of treating low back pain effectively. Despite numerous therapies available, many have only shown modest benefits or inconclusive results. You may find it important to acknowledge that more targeted research is necessary to fully understand low back pain and develop effective treatments tailored to individual needs.
Gaps in Current Studies
Around the landscape of existing research, significant gaps remain. Many commonly used treatments lack high-quality, large-scale placebo-controlled trials, making it difficult for you to find reliable guidance on effective interventions. These inadequacies limit the understanding of how various factors contribute to low back pain and their respective efficacy.
Future Directions
By focusing on personalized medicine, future research should aim to unravel the complexity behind individual responses to treatment. This means identifying distinct pain mechanisms and exploring tailored approaches for management initiatives that yield optimal results for your unique situation.
Also, multidisciplinary care, which combines physical, psychological, and medication therapies, is expected to gain more attention in upcoming studies. This holistic approach acknowledges that pain management is not one-size-fits-all, and you might benefit from a combination of treatments rather than relying on a single option. Investing in further research may lead to breakthroughs in understanding and addressing your pain more effectively, paving the way for new interventions that truly enhance your quality of life.
Conclusion
Now that you know many treatments for lower back pain may not be as effective as hoped, it’s important to stay informed about your options. While some therapies show only modest benefits, understanding your unique pain mechanisms can guide you to more suitable solutions. Consider a multidisciplinary approach to manage your back pain better, which may include physical, psychological, and medication strategies tailored to your needs. Your journey towards relief is personal, and keeping track of what enhances your quality of life can lead to better outcomes in your overall health.
FAQ
Q: What did the recent study reveal about the effectiveness of treatments for back pain?
A: The study found that many treatments for lower back pain, including both medication and non-drug therapies, offer only modest benefits at best. Specifically, while nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) were effective for acute low back pain, only five therapies showed effectiveness for chronic back pain, and these benefits were small compared to placebo. Several therapies, including exercise, steroid injections, and acetaminophen, were identified as ineffective for acute pain, indicating a need for further research to develop targeted treatments.
Q: Why is it important to consider individual responses to back pain treatments?
A: Individual responses to treatments can vary significantly, meaning that while a particular therapy might show little average benefit in studies, it could still help certain patients based on their unique pain mechanisms and preferences. This underscores the importance of personalized approaches in pain management. Healthcare providers often recommend exploring various therapies or combinations to find what best improves a patient’s quality of life, rather than solely focusing on pain reduction scores.
Q: What approach is suggested for managing lower back pain effectively?
A: Multidisciplinary care is recommended for managing lower back pain effectively. This approach incorporates physical, psychological, and medication strategies tailored to the individual needs of the patient. There isn’t a single treatment option that works for everyone, so it is vital to maintain modest expectations and be open to trying different therapies or combinations to identify what works best for each individual.